DEG analysis without biological Replication
https://www.researchgate.net/post/DEG_analysis_without_biological_Replication
DEG analysis without biological Replication
https://www.researchgate.net/post/DEG_analysis_without_biological_Replication
https://hub.docker.com/u/biocontainers/

https://bitesizebio.com/24581/what-is-a-ct-value/
Ct – threshold cycle
Cp – crossing point
TOP – take-off point
Cq – quantification cycle
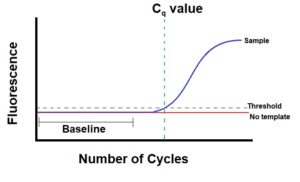
Good summary for qRT-PCR
Rn value
https://www.qiagen.com/us/resources/faq?id=ee18399a-b88b-43ef-9929-27d79ef9ed09&lang=en
The Rn value, or normalized reporter value, is the fluorescent signal from SYBR Green normalized to (divided by) the signal of the passive reference dye for a given reaction. The delta Rn value is the Rn value of an experimental reaction minus the Rn value of the baseline signal generated by the instrument. This parameter reliably calculates the magnitude of the specific signal generated from a given set of PCR conditions. For more information, please refer to your cycler's user manual.
BMC Bioinformatics volume 12, Article number: 323 (2011)
https://bmcbioinformatics.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Bioinformatics, Volume 26, Issue 4, 15 February 2010, Pages 493–500
https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp692
RSEM tutorial